Apple Watch ECG functionality is revolutionizing how we monitor our heart health, offering a glimpse into the future of personal health technology. This innovative feature, now available on select Apple Watch models, allows users to take an electrocardiogram (ECG) directly from their wrist, providing valuable insights into their heart rhythm. From its humble beginnings, this technology has rapidly evolved, targeting a broad audience seeking proactive health management.
The ECG feature’s development reflects Apple’s commitment to merging technology with well-being. Designed with ease of use in mind, it empowers users to take control of their heart health. It aims to make advanced medical monitoring accessible to anyone who wants to keep track of their health, providing a convenient and potentially life-saving tool in a sleek, wearable device.
Introduction to Apple Watch ECG Functionality
The Apple Watch has revolutionized personal health monitoring, and a key feature contributing to this is its electrocardiogram (ECG) functionality. This feature allows users to take an ECG directly from their wrist, providing valuable insights into their heart health. This article delves into the specifics of the Apple Watch ECG feature, its technical aspects, medical applications, and user experience.
Explain the basic function of the Apple Watch ECG feature and its purpose.
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
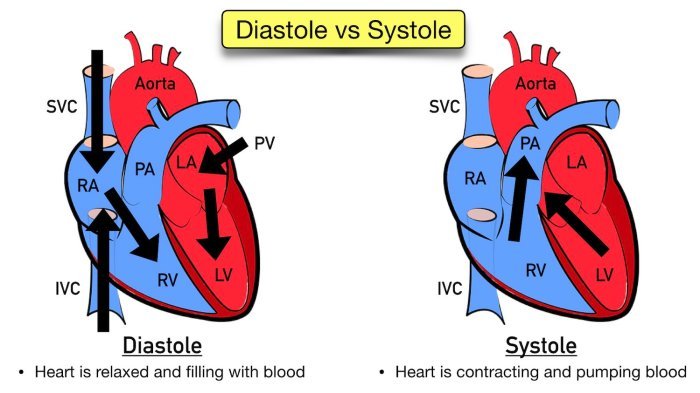
The Apple Watch ECG feature is designed to record the electrical activity of your heart. It functions similarly to a single-lead ECG, which can detect irregularities in your heart rhythm. The primary purpose of the ECG feature is to identify potential signs of atrial fibrillation (AFib), a common type of irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications.
It also aims to provide users with a simple way to monitor their heart health and share this information with their healthcare providers.
Provide a brief history of the ECG feature’s development on the Apple Watch.
The ECG feature was introduced with the Apple Watch Series 4 in 2018. This marked a significant milestone in wearable technology, as it was the first over-the-counter device to offer ECG functionality. The development involved collaboration with medical experts and extensive clinical trials to ensure accuracy and reliability. Subsequent generations of the Apple Watch have maintained and improved this functionality, refining both the hardware and software to enhance the user experience and the accuracy of readings.
Share the intended user demographic for the Apple Watch ECG functionality.
The Apple Watch ECG feature is primarily targeted at adults who are concerned about their heart health or have a history of heart conditions. It’s particularly beneficial for individuals over 65, as the risk of AFib increases with age. The feature is also useful for those who experience symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath, which may indicate an irregular heartbeat.
It is not intended for use by people under 22 years old.
Technical Aspects of ECG Measurement
Understanding how the Apple Watch measures your heart’s electrical activity is crucial to appreciating its functionality. This section explores the underlying technology, from the sensors used to the signal pathways within the device.
Detail the mechanism by which the Apple Watch measures an ECG.
The Apple Watch measures an ECG using an electrode built into the Digital Crown and another electrode on the back of the watch. When the user places their finger on the Digital Crown, a closed circuit is created. The watch then measures the electrical signals that travel across the heart. This signal is then processed by the watch’s software to determine if there are any signs of AFib or other irregularities.
Elaborate on the electrodes and sensors involved in the ECG reading.
The Apple Watch uses two main electrodes: one is located on the back of the watch, which is in contact with the wrist, and the other is built into the Digital Crown. These electrodes are made of a material that can detect the electrical signals generated by the heart. The sensors within the watch amplify these signals and filter out noise to provide a clear ECG reading.
The watch also uses other sensors, such as an accelerometer, to detect movement that could affect the accuracy of the reading.
Design a simplified diagram illustrating the ECG signal pathway within the Apple Watch.
Here’s a simplified explanation of the ECG signal pathway:
- Step 1: The user touches the Digital Crown, completing the circuit.
- Step 2: Electrical signals from the heart are detected by the electrodes.
- Step 3: The signals are amplified and filtered by the watch’s sensors.
- Step 4: The processed data is analyzed by the watch’s software.
- Step 5: The results are displayed on the watch screen and stored in the Health app.
Medical Conditions Detected
The Apple Watch ECG feature is designed to identify specific heart conditions. Understanding these conditions and how the feature aids in their detection is essential for users. However, it is important to remember that the Apple Watch ECG is not a diagnostic tool.
Identify the specific heart conditions the Apple Watch ECG feature is designed to detect.
The primary condition the Apple Watch ECG feature is designed to detect is atrial fibrillation (AFib). AFib is an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications. The ECG feature can also detect other irregularities, although it is not designed to diagnose them.
Provide examples of how the ECG feature helps in the early detection of these conditions.
The Apple Watch ECG feature allows users to take an ECG reading at any time, providing a convenient way to monitor their heart rhythm. If the watch detects signs of AFib, it will alert the user. This early detection can prompt users to seek medical attention and receive appropriate treatment, potentially preventing serious health complications. For example, if a user experiences palpitations, they can take an ECG reading and, if AFib is detected, consult their doctor immediately.
Organize a list using bullet points outlining the limitations of the Apple Watch ECG feature in diagnosing certain conditions.
- Limited Lead: The Apple Watch ECG is a single-lead ECG, which provides less information than a traditional 12-lead ECG.
- Not a Diagnostic Tool: The Apple Watch ECG is not designed to diagnose all heart conditions.
- Interference: Factors such as movement, poor contact with the skin, and certain medications can affect the accuracy of the readings.
- False Positives/Negatives: The feature can produce false positives (indicating AFib when it’s not present) or false negatives (missing AFib).
- Age Limitations: The feature is not intended for use by people under 22 years old.
Using the Apple Watch ECG Feature: Step-by-Step
Taking an ECG reading with the Apple Watch is a straightforward process. This section provides a step-by-step guide to help users understand how to use the feature and interpret the results.
Create a step-by-step guide on how to take an ECG reading using the Apple Watch.
- Ensure Proper Fit: Make sure your Apple Watch fits snugly on your wrist.
- Open the ECG App: Open the ECG app on your Apple Watch. If the app is not installed, make sure you have a supported Apple Watch model and an iPhone.
- Place Your Arm: Rest your arm on a table or in your lap.
- Touch the Digital Crown: Place your finger on the Digital Crown. You don’t need to press it, just touch it.
- Wait for the Reading: Hold still for 30 seconds while the watch records your ECG.
- View the Results: After 30 seconds, you will see the results on your watch screen.
Demonstrate how to interpret the results provided by the Apple Watch.
The Apple Watch will provide one of the following results:
- Sinus Rhythm: This means your heart rhythm is regular, and the watch did not detect any signs of AFib.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): This indicates that the watch detected an irregular heart rhythm, which may be AFib.
- Inconclusive: This means the reading is not clear, possibly due to poor contact, movement, or other factors.
- Low or High Heart Rate: This indicates that your heart rate is either too low or too high, which may require medical attention.
Provide examples of different ECG readings and their meanings.
- Example 1: The watch shows “Sinus Rhythm.” This indicates a normal heart rhythm. The user doesn’t need to take any action.
- Example 2: The watch shows “Atrial Fibrillation (AFib).” The user should consult a doctor to discuss the results.
- Example 3: The watch shows “Inconclusive.” The user should try taking another reading. If the result remains inconclusive, they should consult a doctor.
Regulatory Approvals and Certifications
The Apple Watch ECG feature has received regulatory approvals in various regions, signifying its safety and effectiveness. Understanding these approvals is essential for users, as they impact the availability and use of the feature.
Discuss the regulatory approvals (e.g., FDA, CE) the Apple Watch ECG feature has received.
The Apple Watch ECG feature has received significant regulatory approvals, including clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and CE marking in Europe. These approvals confirm that the feature meets the necessary standards for safety and performance. The FDA approval was a landmark, as it was the first over-the-counter ECG device to receive such clearance. CE marking allows the Apple Watch to be sold and used in the European Economic Area.
Explain the significance of these approvals in different regions.
These regulatory approvals are crucial for several reasons:
- Safety and Efficacy: Approvals ensure that the device has been tested and proven to be safe and effective in detecting AFib.
- Market Access: Regulatory clearance allows Apple to sell the Apple Watch with the ECG feature in those regions.
- Trust and Credibility: Regulatory approvals provide confidence to users and healthcare professionals that the device is reliable.
Compare and contrast the regulatory landscape for medical devices in the US and Europe using a table with up to 4 responsive columns.
| Feature | United States (FDA) | Europe (CE Marking) | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Body | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) | Notified Bodies (e.g., TÜV SÜD, BSI) | Both are essential for market access and ensuring device safety. |
| Approval Process | Pre-market notification (510(k)) or premarket approval (PMA) | Conformity assessment by a Notified Body | US requires more rigorous pre-market testing for higher-risk devices. |
| Standards | Follows FDA guidelines and standards. | Complies with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) | Both regions have high standards for device safety and performance. |
| Post-Market Surveillance | FDA monitors device performance and safety through reporting. | MDR emphasizes post-market surveillance and vigilance. | Both regions monitor device performance after market entry. |
Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of the Apple Watch ECG feature are crucial for its usefulness. This section explores the feature’s performance compared to traditional ECGs and factors that can affect the results.
Discuss the accuracy of the Apple Watch ECG feature compared to a traditional 12-lead ECG., Apple Watch ECG functionality
The Apple Watch ECG feature has demonstrated a high degree of accuracy in detecting AFib. Studies have shown that the feature can accurately identify AFib with a sensitivity and specificity that is comparable to traditional ECGs. However, it’s important to note that the Apple Watch ECG is a single-lead ECG, which provides less information than a 12-lead ECG used in a clinical setting.
A 12-lead ECG provides a more comprehensive view of the heart’s electrical activity, allowing for the detection of a wider range of heart conditions.
Provide information on factors that can affect the accuracy of the ECG readings.
Several factors can affect the accuracy of the Apple Watch ECG readings:
- Movement: Moving during the reading can introduce artifacts and affect the results.
- Poor Contact: Ensuring good contact between the watch and your wrist/finger is crucial.
- Skin Conditions: Skin conditions like eczema can interfere with the signal.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect heart rhythm and the accuracy of the readings.
- Technical Issues: Problems with the watch hardware or software can also affect accuracy.
Share research studies or clinical trials related to the reliability of the Apple Watch ECG feature.
Several studies have been conducted to evaluate the reliability of the Apple Watch ECG feature. One study published in the “Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)” found that the Apple Watch ECG feature had a high sensitivity and specificity for detecting AFib. Another study showed that the Apple Watch could accurately identify AFib in a real-world setting. These studies support the feature’s reliability and its potential for early detection of heart conditions.
Potential Benefits and Risks
The Apple Watch ECG feature offers several potential benefits but also carries some risks and limitations. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages is crucial for users.
Elaborate on the potential benefits of using the Apple Watch ECG feature.
The Apple Watch ECG feature provides numerous benefits:
- Early Detection: It can help detect AFib early, allowing for timely medical intervention.
- Convenience: Users can take an ECG reading anytime, anywhere.
- Peace of Mind: Regular monitoring can provide reassurance about heart health.
- Data Sharing: Users can easily share their ECG data with their doctors.
- Proactive Health Management: Encourages users to take a more active role in their health.
Identify the potential risks or limitations associated with the feature.
The Apple Watch ECG feature has some limitations:
- False Positives/Negatives: The feature can sometimes produce inaccurate results.
- Not a Diagnostic Tool: It is not a substitute for a medical diagnosis.
- Limited Information: The single-lead ECG provides less information than a 12-lead ECG.
- Reliance on Technology: Users may become overly reliant on the feature.
- Requires Interpretation: Results need to be interpreted by a healthcare professional.
Discuss the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional based on the ECG results.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if the Apple Watch ECG feature detects an irregular heart rhythm or if you have any concerns about your heart health. A doctor can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend further testing, and develop a treatment plan if needed. The Apple Watch ECG is a screening tool, and professional medical advice is essential for accurate interpretation and management of any potential heart conditions.
Integration with Apple Health and Other Apps
The Apple Watch ECG feature seamlessly integrates with the Apple Health app and other related applications, making it easier for users to manage and share their health data. This section explores the data flow and the user’s ability to interact with their ECG information.
Detail how the ECG data is integrated with the Apple Health app.
The Apple Watch ECG data is automatically integrated with the Apple Health app on the user’s iPhone. The Health app stores the ECG readings, along with other health metrics, such as heart rate, activity levels, and sleep data. Users can view their ECG history, track trends over time, and see detailed information about each reading. The app also provides educational resources about heart health and AFib.
Explain how users can share their ECG data with their doctors.
Users can easily share their ECG data with their doctors through the Apple Health app. They can generate a PDF report of their ECG readings, which can be sent via email or shared through other communication channels. Users can also share their Health data directly with their doctors if they use a compatible electronic health record (EHR) system. This seamless data sharing facilitates better communication and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers.
Design a visual representation showing the flow of ECG data within the Apple ecosystem.
Here’s a simplified diagram illustrating the flow of ECG data:
- Apple Watch: Records ECG data.
- iPhone: Data is synced to the Health app.
- Health App: Stores and displays ECG data, including readings and results.
- User: Views and shares data.
- Doctor/Healthcare Provider: Receives and reviews data.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the Apple Watch ECG functionality represents a significant leap forward in personal health monitoring. By seamlessly integrating advanced technology into a user-friendly device, Apple has opened doors to early detection of potential heart conditions and proactive health management. While it’s essential to remember that this feature is not a replacement for professional medical advice, it offers a powerful tool for individuals seeking to understand and protect their heart health, promising a healthier future, one heartbeat at a time.